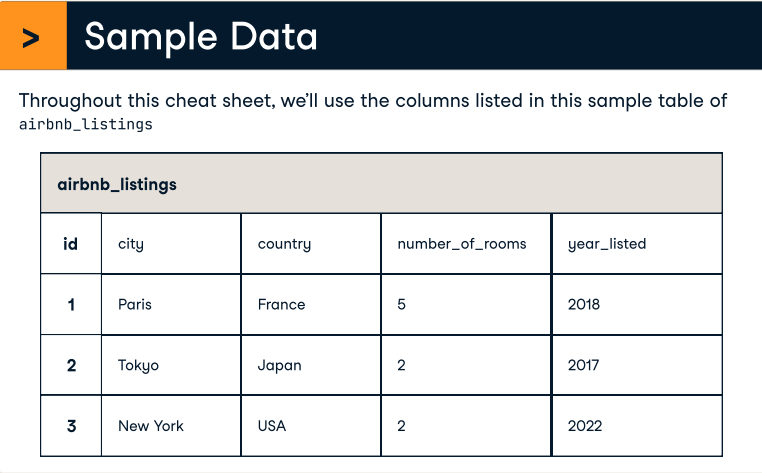
Querying Tables
Getting all columns
SELECT * FROM airbnb_listingsGetting the city column
SELECT city
FROM airbnb_listings;Getting the city and year_listed columns
SELECT city, year_listed
FROM airbnb_listings;Ordering by ascending order
SELECT id, city
FROM airbnb_listings
ORDER BY number_of_rooms ASC;Ordering by descending order
SELECT id, city
FROM airbnb_listings
ORDER BY number_of_rooms DESC;Get the first 5 rows
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
LIMIT 5;Get unique list of cities
SELECT DISTINCT city
FROM airbnb_listings;Filtering data
Filtering numeric columns
Get all listings where number of rooms >= 3
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE number_of_rooms >= 3;- Can be replaced with >, <, ⇐, =
Get all listings where 3 to 6 rooms
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE number_of_rooms BETWEEN 3 and 6;Filtering text columns
Get all listings based in ‘PARIS’—
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE city = 'Paris';Get listings based in the ‘USA’ and ‘France’
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE country IN ('USA', 'France');Get all listings where the city starts with ‘j’ and does not end in ‘t’
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE city LIKE 'j%' AND city NOT LIKE '%t'Filtering multiple columns
Get all listings in ‘Paris’ where number of rooms > 3
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE city = 'Paris' AND number_of_rooms > 3;Get all listings in ‘Paris’ OR ones that were listed after 2012
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE city = 'Paris' OR year_listed > 2012;Filtering missing data
Return listings where number of rooms is missing
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE number_of_rooms IS NULL;Return listings where number of rooms is not missing
SELECT *
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE number_of_rooms IS NOT NULL;Aggregating Data
Simple aggregations
Get total number of rooms available across all listings
SELECT SUM(number_of_rooms)
FROM airbnb_listings;Get average number of rooms per listing across all listings
SELECT AVG(number_of_rooms)
FROM airbnb_listings;Get listing with the highest number of rooms across all listings
SELECT MAX(number_of_rooms)
FROM airbnb_listings;Get Listing with the lowest number of rooms
SELECT MIN(number_of_rooms)
FROM airbnb_listings;Grouping, filtering and sorting
Get total number of rooms for each country
SELECT country, SUM(number_of_rooms)
FROM airbnb_listings
GROUP BY country;Get average number of rooms for each country
SELECT country, AVG(number_of_rooms)
FROM airbnb_listings
GROUP BY country;Get listing with lowest amount of rooms per country
SELECT country, MIN(number_of_rooms)
FROM airbnb_listings
GROUP BY country- Replace with MAX for maximum number of rooms
For each country, get the average number of rooms per listing and sort by ascending order
SELECT country, AVG(number_of_rooms) AS avg_rooms
FROM airbnb_listings
GROUP BY country
ORDER BY avg_rooms ASCFor Japan and USA, get maximum number of rooms per listing in each country
SELECT country, MAX(number_of_rooms)
FROM airbnb_listings
WHERE country IN ('USA', 'Japan')
GROUP BY countryGet number of cities per country where there are listings
SELECT country, COUNT(city) AS number_of_cities
FROM airbnb_listings
GROUP BY countryGet all years where there were more than 100 listings
SELECT year_listed
FROM airbnb_listings
GROUP BY year_listed
HAVING COUNT(id) > 100Get length of string
LENGTH(string)SQL Joins
- Tables are made up of attributes (columns) and records (rows)
- Primary key can uniquely identify a row in a table (single or multiple columns)
- Usually an id column
- Foreign key established relationship with another table’s primary key, usually prepended with the table it is referencing, followed by _id
- Such relationships can be used to join the data in different tables
- For a join, you only need two columns of the same type, whether it is a primary or foreign key does not matter
- This can lead to joining unrelated keys of the same type together
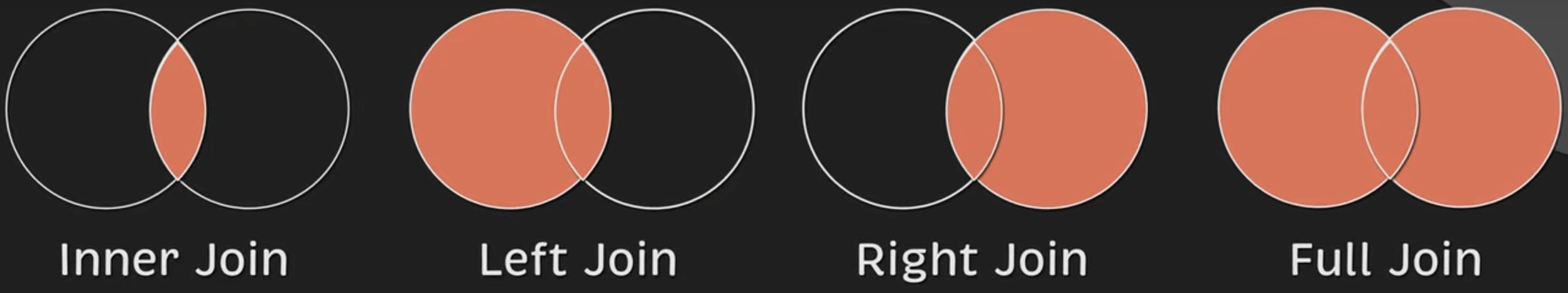
Inner join
- Combines the columns on a common dimension when possible
- Only includes data for the columns that share the same values in the common column
- Will not create a new table with rows that do not have a match
- Default type of join in SQL, INNER JOIN == JOIN
- Duplicate data may occur when the columns we are joining are not unique
Left join
- SQL adds all rows in the left table, including those that do not have a match with the right table, placing null as the values
Right join
- Any right join can be rewritten as a left join
- Same concept as a left join, just that the right table is the main table where we will add all rows regardless if there is a match
Full/Outer join
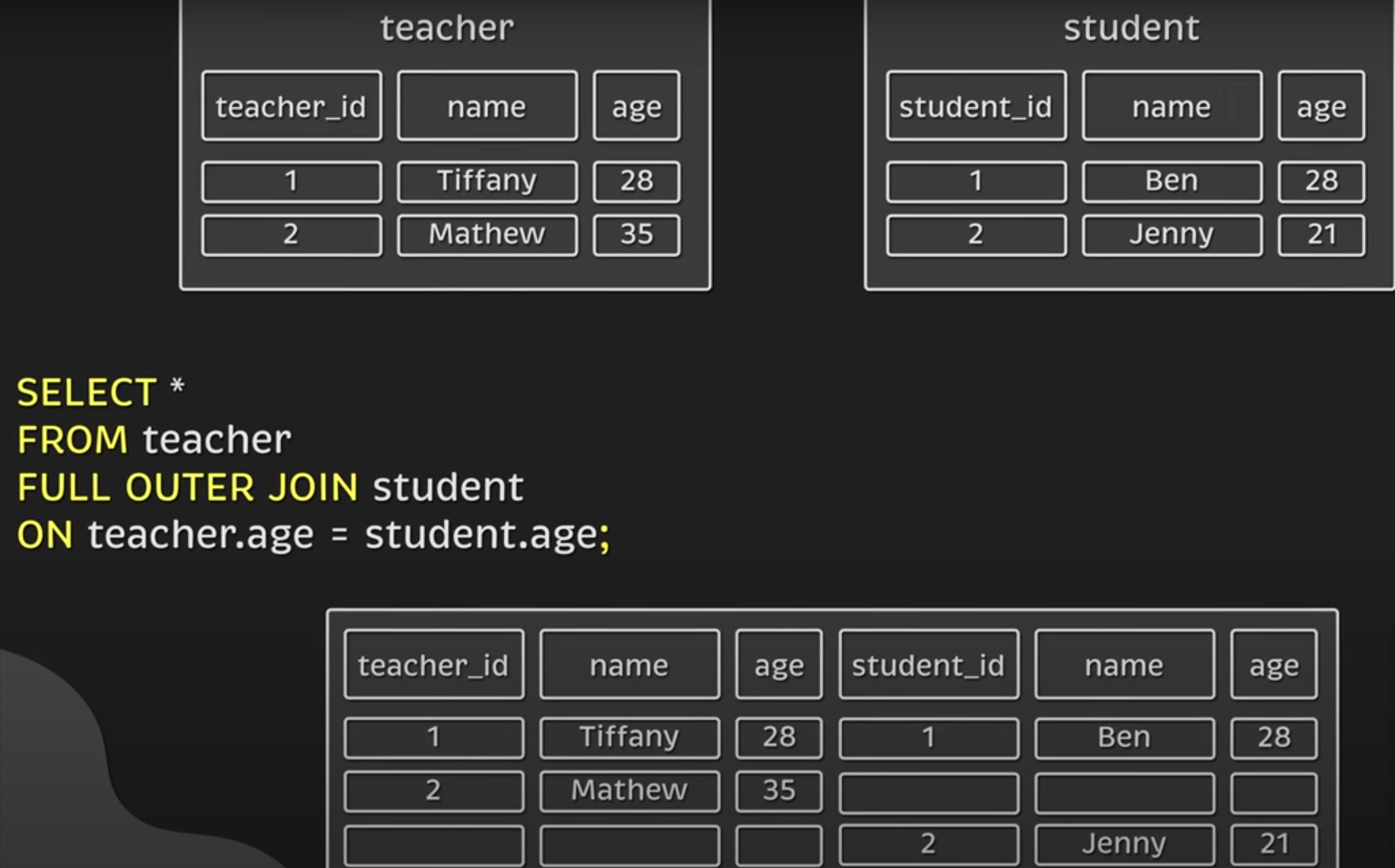
- Merge 2 tables
- Combines columns from all tables based on 1 or more common dimensions
- Basically does a left and right join on both tables
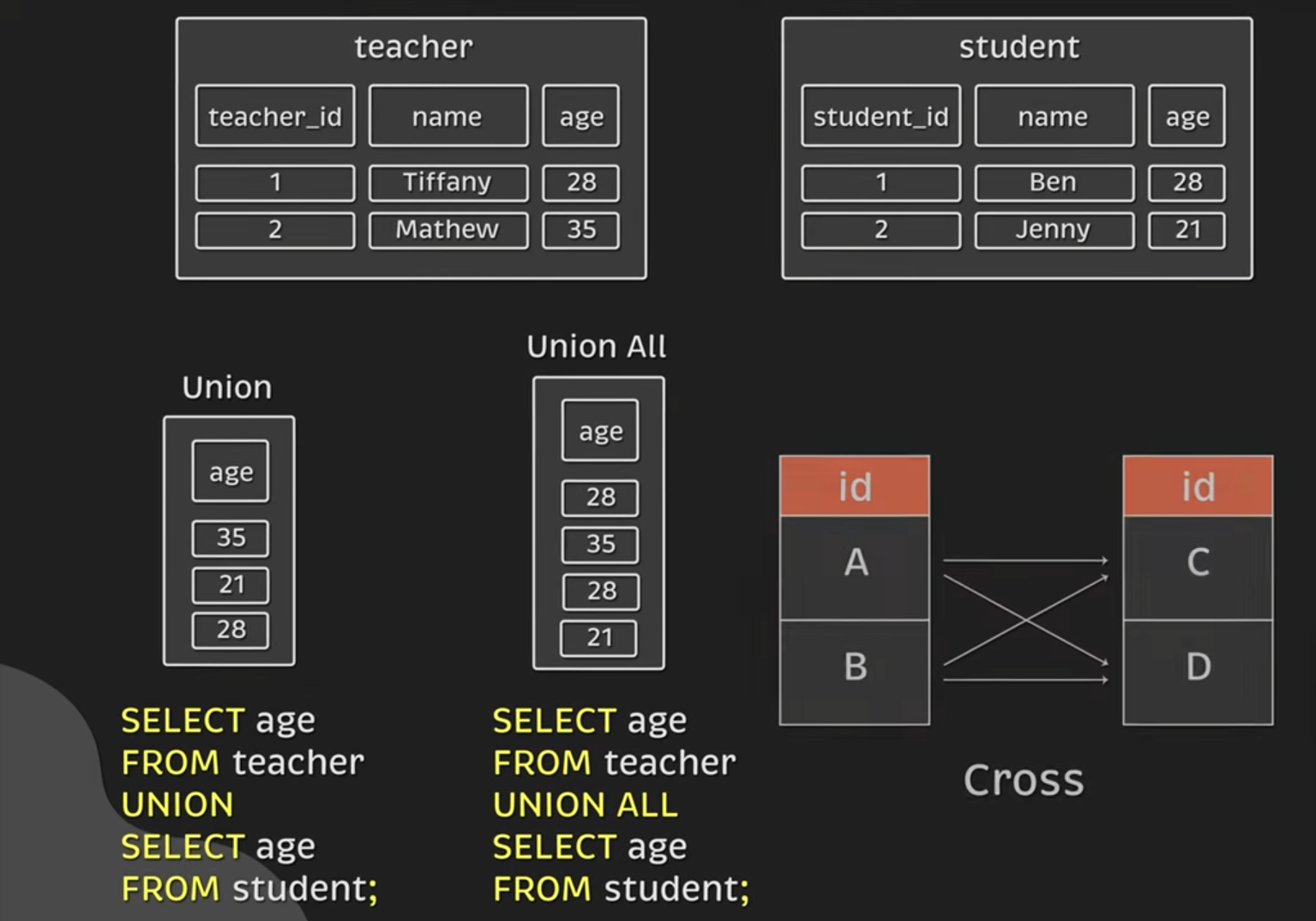
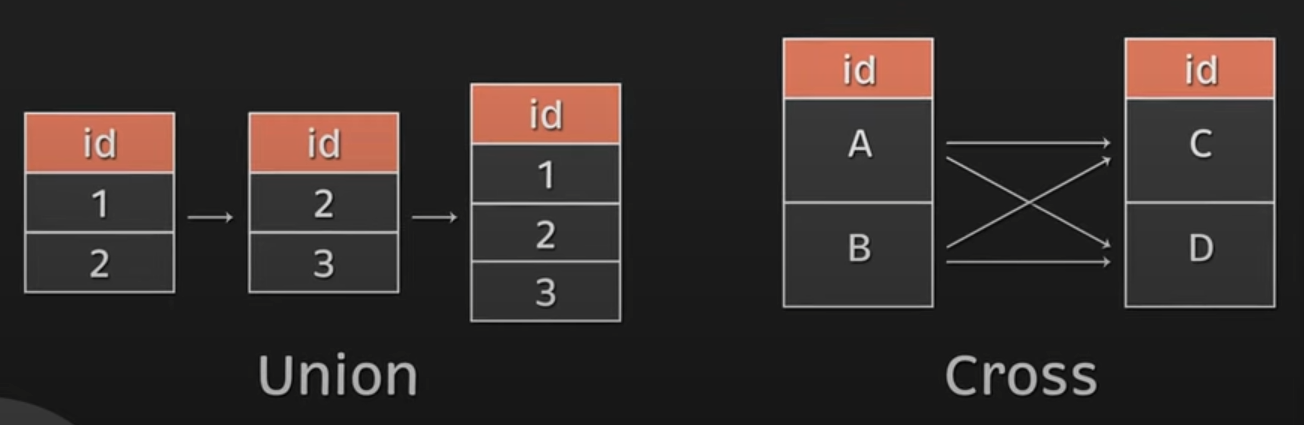
Union
- Does not attach the data from two tables to a single row
- Stacks 2 datasets on top of each other into a single table
- Data types of the columns must be the same as well
- SQL takes all possible values and ignore duplicate fields
Union all
- Same as union, but does not ignore duplicate fields
Cross join

- For each row in the first table, it will attach to every row in the second table
- All possible combinations
- Cartesian product between the 2 columns